Are you tired of your Windows PC restarting frequently? Here are 10 ways to fix this issue and get your computer running smoothly again.
Troubleshooting Software Conflicts and Malware Infections
To troubleshoot software conflicts and malware infections causing frequent PC restarts, start by running a full system scan with a reliable antivirus program to detect and remove any malicious software and malware infections. Check for any recent software installations or updates that may be causing conflicts, and consider uninstalling or rolling back these changes.
Update Windows to ensure that your operating system has the latest patches and security fixes. Use System Restore to revert your system to a previous state where it was functioning properly, if necessary. Check for device driver updates and ensure that all your drivers are up to date.
If you suspect a hardware issue, check your power supply and clean out any dust that may be affecting your system. Lastly, consider seeking professional help if you are unable to resolve the issue on your own.
Addressing Hardware Failures and Power Supply Issues
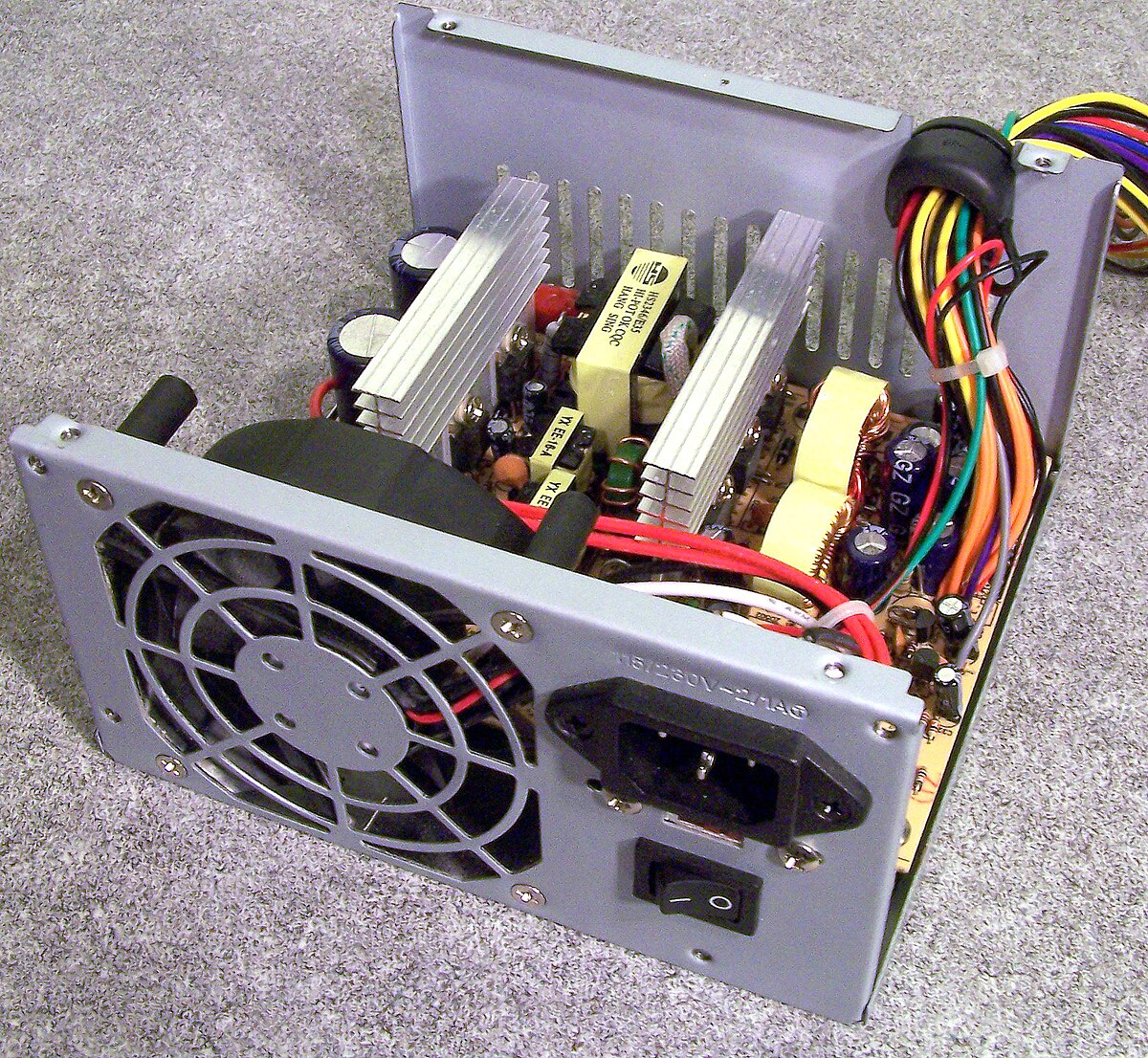
If your Windows PC is restarting frequently, it could be due to hardware failures or power supply issues. Start by checking the power supply for any issues such as loose connections or overheating. Make sure all hardware components are properly connected and functioning.
Check for any error messages or unusual noises coming from the power supply unit. If you suspect a hardware failure, consider running a hardware diagnostic test to identify the problem.
Ensure that the power supply is supplying enough power to all components, especially if you have recently added new hardware. Overloading the power supply can cause frequent restarts.
Inspect the inside of your PC for dust buildup, as this can cause overheating and hardware failures. Use a can of compressed air to clean out any dust from the computer components.
If you have recently installed new hardware or drivers, consider rolling back to a previous version using System Restore. This can help resolve any compatibility issues that may be causing the frequent restarts.
By addressing hardware failures and power supply issues, you can troubleshoot and fix the frequent restarting of your Windows PC.
Disabling Automatic Reboot Features
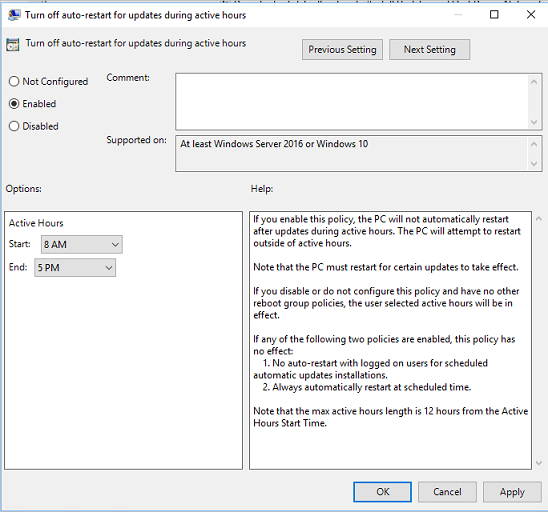
To disable automatic reboot features in Windows PC, follow these steps. First, press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box. Then, type “gpedit. msc” and press Enter. In the Local Group Policy Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows Update.
Double-click on “No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations” and select “Enabled” to prevent automatic reboots. Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes. Finally, restart your computer for the changes to take effect. This should help prevent frequent restarts caused by automatic updates.
Adjusting Advanced Power Settings
To adjust advanced power settings, go to Control Panel and select Power Options. Then, click on Change plan settings next to your selected power plan. After that, select Change advanced power settings to customize options such as sleep, display, and processor power management. Make sure to adjust the settings to optimize your PC’s performance and prevent frequent restarts. Pay attention to settings like hard disk and USB to avoid data loss.
Ensure that your device drivers are up to date to prevent any compatibility issues that could be causing the frequent restarts.
Updating or Reinstalling Graphics and Device Drivers
To update or reinstall your graphics and device drivers, start by accessing the Device Manager. Right-click on the Start button and select Device Manager. Look for the Display Adapters and Sound, Video and Game Controllers sections. Right-click on the device you want to update and select Update Driver. Choose Search automatically for updated driver software. If Windows doesn’t find a new driver, you can manually download and install the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website.
If updating doesn’t work, you can try uninstalling the driver and then reinstalling it. This can help fix issues with corrupted or outdated drivers.
Checking for RAM Errors and Overheating Problems
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Run Windows Memory Diagnostic tool to check for RAM errors |
| 2 | Use third-party software to test RAM for errors |
| 3 | Clean the computer’s internal components to prevent overheating |
| 4 | Check for dust and blockages in the computer’s cooling system |
| 5 | Monitor the computer’s temperature using software |
Updating BIOS to Resolve Boot Issues
Updating your BIOS can help resolve boot issues on your Windows PC. To do this, visit the manufacturer’s website and download the latest BIOS update for your specific model. Make sure to follow the instructions carefully and back up your data before proceeding. Once the update is complete, restart your computer and check if the boot issues have been resolved.
Keep in mind that updating the BIOS carries some risk, so it’s essential to proceed with caution and ensure that the update is necessary for resolving the frequent restarts.