In this article, I will discuss how to fix high memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10/11.
Understanding High Memory Usage
Understanding High Memory Usage: When experiencing high memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10 or 11, it’s important to identify the culprit. Look for any programs or processes consuming a large amount of memory. Check for memory leaks or inefficient coding in applications that may be causing the issue. Consider restarting your computer to free up memory and close unnecessary programs running in the background. Monitor your memory usage regularly to catch any spikes or abnormal behavior.
If the problem persists, you may need to investigate further or seek professional help.
Symptoms and Causes of High Memory Usage
Symptoms of high memory usage in Windows 10/11 can include sluggish performance, freezing, and error messages related to low memory. Causes may include running too many programs simultaneously, memory leaks in applications, malware infections, or outdated hardware drivers.
Common symptoms of high memory usage include slow performance, freezing, and error messages related to low memory. High memory usage can be caused by running too many programs simultaneously, memory leaks in applications, malware infections, or outdated hardware drivers.
If you notice your computer is slow or unresponsive, check the Task Manager to identify which processes are using the most memory. Look for any programs that are using an unusually high amount of memory and consider closing them to free up memory resources.
Memory leaks can occur when a program fails to release memory it no longer needs, leading to an increase in memory usage over time. Updating the application or restarting your computer can help resolve memory leaks.
Malware infections can also cause high memory usage. Run a full system scan using an antivirus program to check for any malicious software that may be using up system resources.
Outdated hardware drivers can also contribute to high memory usage. Update your drivers to ensure compatibility with the latest software updates and optimize memory management on your system.
By identifying the symptoms and causes of high memory usage in Windows 10/11, you can take steps to fix the issue and improve the performance of your computer.
Closing Unnecessary Programs and Applications
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc
- Alternatively, you can right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” from the menu
- Click on the “Processes” tab to see a list of all running programs and applications
- Sort the list by memory usage by clicking on the “Memory” column header
- Identify any programs or applications using a large amount of memory
- Right-click on the program or application and select “End Task” to close it
- Repeat this process for any other programs or applications that are using a significant amount of memory
- Check the Task Manager again to see if memory usage has decreased
Managing Startup Programs
To manage startup programs in Windows 10/11 and fix high memory usage, you can use the Task Manager. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager. Go to the “Startup” tab to see which programs are set to launch at startup. Disable unnecessary programs by right-clicking on them and selecting “Disable.” This can help reduce memory usage and improve system performance.
Another way to manage startup programs is by using the Windows Registry. Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, then type “regedit” and press Enter. Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run and HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run to see startup programs. Delete the keys of programs you don’t want to launch at startup.
If you suspect a computer virus causing high memory usage, run a full antivirus scan using a reliable antivirus program. Additionally, you can use tools like Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software to remove any malicious files causing the issue.
Ensure your system is up to date by installing the latest Windows updates. These updates often include patches and fixes that can help optimize memory management and resolve memory-related issues. Regularly check for updates through the Windows Update settings.
Adjusting for Best Performance
To adjust for best performance in Windows 10/11 Task Manager, follow these steps:
1. Disable Startup Programs: Open Task Manager, go to the Startup tab, and disable unnecessary programs from starting up with your computer.
2. Check Resource Usage: Monitor which programs are using the most memory and CPU in Task Manager’s Processes tab.
3. Update Drivers: Ensure all your drivers are up to date by checking for updates on the manufacturer’s website.
4. Adjust Virtual Memory: Go to System Properties > Advanced System Settings > Performance Settings > Advanced > Virtual Memory, and adjust the paging file size.
5. Scan for Malware: Run a full system scan with your antivirus software to check for any potential malware causing high memory usage.
6. Clean up Disk: Use Disk Cleanup to remove unnecessary files and free up space on your hard drive.
Defragmenting Hard Drives
Defragmenting your hard drive can help improve memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10/11. To defragment your hard drive:
First, open the Start menu and type “Defragment and Optimize Drives” in the search bar. Press Enter to open the Disk Defragmenter tool.
Next, select the drive you want to defragment and click on “Optimize.” This will rearrange the data on your drive to make it more efficient.
Wait for the process to complete, which may take some time depending on the size and fragmentation level of your drive.
Once the defragmentation is done, check Task Manager again to see if memory usage has improved. Repeat this process regularly to keep your hard drive optimized.
Defragmenting your hard drive can help speed up your computer and reduce memory usage, so make it a part of your regular maintenance routine.
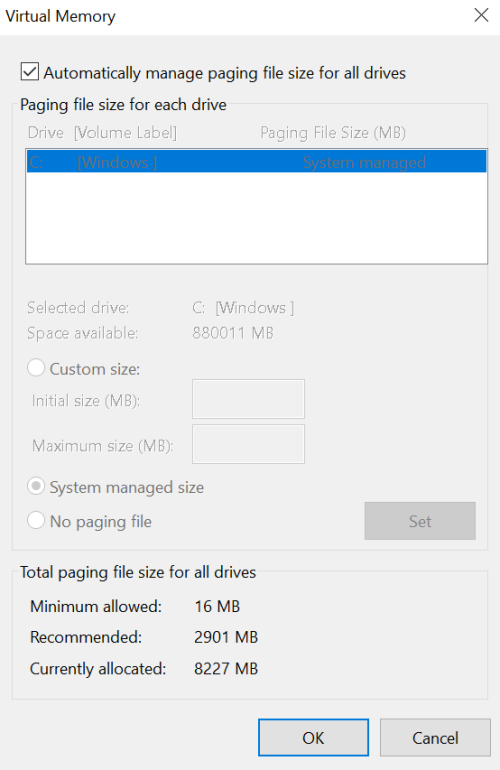
Increasing Virtual Memory
![]()
To increase virtual memory on Windows 10/11, you can follow these steps:
1. Right-click on “This PC” or “My Computer” and select “Properties.”
2. In the System Properties window, go to the “Advanced” tab.
3. Under the Performance section, click on “Settings.”
4. In the Performance Options window, go to the “Advanced” tab.
5. Under the Virtual Memory section, click on “Change.”
6. Uncheck the box that says “Automatically manage paging file size for all drives.”
7. Select the drive where you want to increase the virtual memory.
8. Click on “Custom size” and enter a higher value for the initial and maximum size.
9. Click “Set” and then “OK” to save the changes.
10. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Disabling Superfetch Service

To disable the Superfetch service and fix high memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10/11, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “services.msc” and hit Enter to open the Services window.
3. Scroll down and locate the Superfetch service in the list.
4. Right-click on Superfetch and select Properties.
5. In the General tab, change the Startup type to Disabled.
6. Click Apply and then OK to save the changes.
7. Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Disabling Superfetch can help reduce high memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10/11.
Conducting Full-System Scans for Viruses
It is recommended to use a reliable antivirus software to perform a thorough scan of your system. Make sure the antivirus program is up-to-date to detect the latest threats.
After initiating the scan, allow the antivirus software to complete the process. This may take some time depending on the size of your system and the number of files being scanned.
Once the scan is complete, review the results to see if any viruses or malware were detected. Take appropriate action to remove or quarantine any threats found to improve your system’s performance.
Modifying Registry Settings
To modify Registry settings, open the Registry Editor by pressing Windows key + R and typing “regedit” in the Run dialog box. Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Memory Management. Look for ClearPageFileAtShutdown and set its value to 1 to clear the page file on shutdown. You can also adjust the PagedPoolSize and PoolUsageMaximum values to optimize memory usage.
Expanding Physical Memory
To expand physical memory on Windows 10/11 and fix high memory usage in Task Manager, you can try adding more RAM to your computer. Increasing the amount of RAM will help improve overall system performance and reduce memory usage. Make sure to check your computer’s specifications to ensure compatibility with the new RAM.
Another way to expand physical memory is by using a USB drive as ReadyBoost. Insert a USB drive into your computer and configure it as ReadyBoost to help increase the available memory. This can be an effective solution for systems with limited RAM.
Additionally, you can try optimizing your computer’s virtual memory settings. Adjust the virtual memory settings in Control Panel to allocate more space on your hard drive for virtual memory. This can help manage memory usage more efficiently.
If you are still experiencing high memory usage after trying these methods, consider running a diagnostic scan for malware and viruses. Use a reliable antivirus program to scan your computer and remove any malicious software that may be causing high memory usage. Regularly scan your system to prevent future issues.
By expanding physical memory and following these steps, you can effectively fix high memory usage in Task Manager on Windows 10/11.
Reinstalling or Rolling Back Windows
To reinstall Windows: First, back up all your important files to avoid losing any data. Then, insert the Windows installation disk or USB drive and restart your computer. Follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall Windows. Remember to activate Windows once the installation is complete.
To roll back Windows: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery. Click on ‘Get started’ under ‘Go back to the previous version of Windows 10/11’. Follow the instructions to roll back to the previous version. Keep in mind that this option is only available for a limited time after updating Windows.
If you are still experiencing high memory usage after reinstalling or rolling back Windows, consider checking for any malware using a reliable antivirus program and optimizing your system by removing unnecessary startup programs and disabling any unnecessary services.
Preventative Tips for High Memory Usage
To prevent high memory usage in Windows 10/11, follow these preventative tips:
1. Close unnecessary programs and browser tabs to free up memory.
2. Check for malware using Windows Defender or another antivirus program.
3. Update your drivers and Windows to ensure compatibility and performance.
4. Disable startup programs that consume memory unnecessarily.
5. Use the Task Manager to monitor memory usage and identify resource-intensive processes.
6. Adjust virtual memory settings to optimize memory usage.
7. Clear temporary files and cache to free up space.
8. Consider upgrading your RAM if memory usage remains high.
FAQs
How do I fix high memory usage in Task Manager?
To fix high memory usage in Task Manager, you can start by closing excessive programs, reducing the number of startup programs, checking if Superfetch is disabled, selecting best performance options, defragging your hard drives, increasing total paging file size, releasing virtual memory by setting a registry hack, and conducting a full-system scan.
Why is my RAM usage so high when nothing is running?
Your RAM usage is high even when nothing is running because it is being used for caching recently-accessed disk data and storing kernel data structures like filesystem metadata to prevent them from being re-generated when needed.
Why is my memory showing 100 in Task Manager?
Your memory is showing 100 in Task Manager because there may be malware or unnecessary background processes causing your hard drive to run at full speed needlessly.
Is 40 percent memory usage normal?
It is considered normal for RAM usage to be around 30% to 50% when idle in Task Manager.