Are you frustrated with the slow performance of your Windows 10 PC? Here are some practical solutions to help improve its speed and efficiency.
Optimize Power Settings
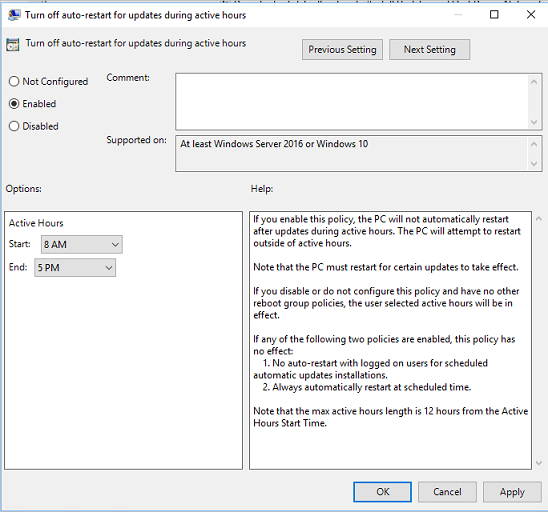
To improve the performance of your Windows 10 PC, optimizing the power settings can make a significant difference. By adjusting the power settings, you can prioritize performance over energy saving and enhance the overall speed and responsiveness of your computer.
Here are some steps to optimize power settings in Windows 10:
1. Open the Control Panel by typing “Control Panel” in the search bar and selecting it from the results.
2. In the Control Panel, click on “Power Options.”
3. Select the power plan that suits your needs. You can choose between Balanced, Power Saver, and High Performance. For better performance, select the High Performance power plan.
4. Customize the power plan by clicking on “Change plan settings” next to the selected power plan.
5. Adjust the settings according to your preferences. For example, you can set the display and sleep times to longer intervals to prevent your PC from entering low power states too quickly.
6. Click on “Change advanced power settings” to access more options.
7. In the Advanced settings, you can fine-tune various power options. Expand the categories and modify the settings based on your requirements.
8. To disable background applications that consume power, go to the “Multimedia settings” category and set “When playing video” and “When playing audio” to “Optimize performance.”
9. Adjust the processor power management settings under the “Processor power management” category. Set the minimum and maximum processor state to 100% for maximum performance.
10. Disable USB selective suspend to prevent USB devices from entering a low power state. Expand the “USB settings” category and set “USB selective suspend setting” to “Disabled.”
11. Apply the changes and exit the Control Panel.
By optimizing the power settings, you can ensure that your Windows 10 PC is operating at its full potential. This can help eliminate any sluggishness or lag you may have been experiencing.
Remember to periodically check for Windows updates as these can include performance improvements and bug fixes that can further enhance your PC’s performance.
Additionally, consider keeping your computer hardware clean and free from dust, as excessive heat can also impact performance. Regularly defragmenting your hard disk drive and using tools like ReadyBoost to improve disk performance can also help.
Following these steps and implementing these optimizations can significantly improve the speed and performance of your Windows 10 PC, allowing you to enjoy a smoother and more efficient computing experience.
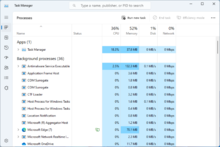
Manage Startup Programs

- Identify unnecessary startup programs
- Access the Task Manager
- Click on the “Startup” tab
- Disable unwanted startup programs
- Right-click on the program
- Select “Disable” from the context menu
- Enable essential startup programs
- Right-click on the program

- Select “Enable” from the context menu
- Consider removing non-essential programs from startup
- Restart your computer
Restore Previous System State
To restore the previous system state on Windows 10 and fix slow PC performance, follow these steps:
1. Open the Control Panel by clicking on the Start button and typing “Control Panel”. Press Enter to open it.
2. In the Control Panel, click on “System and Security” and then on “System”.
3. In the System window, click on “System Protection” on the left-hand side.
4. In the System Properties window, under the “System Protection” tab, click on “System Restore”.
5. Click on “Next” in the System Restore window.
6. You will see a list of restore points available. Choose a restore point that you believe will help fix the slow PC performance. Typically, it is recommended to choose the most recent restore point before the performance issue started.
7. Click on “Next” and then on “Finish” to start the system restore process.
8. Windows will restart your computer and begin the system restore process. This may take some time, so be patient.
9. Once the system restore process is complete, Windows will restart again. After the restart, check if the PC performance has improved.
10. If the performance issue persists, you may need to try other troubleshooting methods or consider seeking professional help.
Remember to regularly create restore points to have a recent backup of your system state. This can be done by following the same steps mentioned above and clicking on “Create” in the System Protection tab.
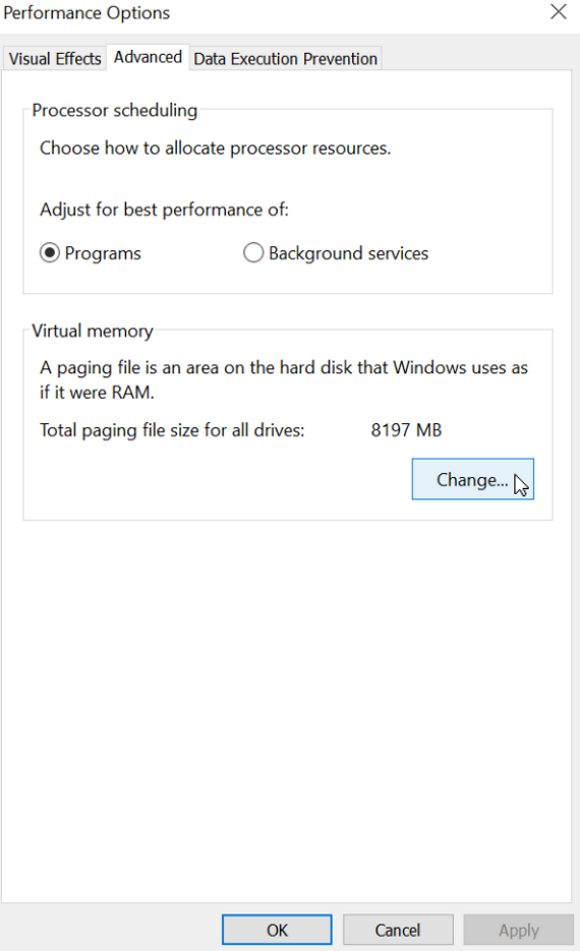
Enhance Disk Caching with ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost is a feature in Windows 10 that can significantly improve your PC’s performance by using a USB flash drive or SD card as additional cache memory. This can be particularly helpful if you have a slow PC and want to speed up disk access times.
To enhance disk caching with ReadyBoost, follow these steps:
1. Connect a USB flash drive or insert an SD card into your computer. Make sure it has enough free space to be used for caching.
2. Right-click on the drive in File Explorer and select “Properties.”
3. In the Properties window, go to the “ReadyBoost” tab.
4. Check the box that says “Use this device” and adjust the slider to allocate the desired amount of space for caching. Keep in mind that ReadyBoost works best with at least 1-2 GB of cache space.
5. Click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
By enabling ReadyBoost, Windows will use the USB flash drive or SD card as additional cache memory, which can help speed up disk access times and improve overall performance.
It’s important to note that ReadyBoost is most effective on systems with low memory (RAM) and slower hard drives. If you have a fast SSD or ample RAM, the benefits of ReadyBoost may be minimal.
Additionally, if you have an external hard drive connected to your computer, it’s recommended to disable ReadyBoost for that drive. ReadyBoost is designed to work best with flash-based storage devices, not traditional hard disk drives.
Remember to periodically check the performance of your computer and adjust the ReadyBoost settings if needed. As your usage patterns change or if you add more memory to your system, you may want to reevaluate the allocated cache space.
By following these steps, you can enhance disk caching with ReadyBoost and potentially improve the performance of your Windows 10 PC. Give it a try and see if it makes a difference for you.
If you have any further questions or encounter any issues, refer to the Windows 10 documentation or consult Microsoft’s support resources for troubleshooting tips.
Remember, ReadyBoost is just one of many potential solutions for improving PC performance. Be sure to also consider other factors such as OneDrive syncing, regular defragmentation, installing Windows updates, and optimizing your startup programs.
Efficient disk caching can have a significant impact on your PC’s overall performance, so it’s worth exploring different options and finding what works best for your specific setup.
Turn Off Windows Tips
1. Open the Settings app by pressing the Windows key + I on your keyboard.
2. In the Settings window, click on “System” and then select “Notifications & actions” from the left-hand menu.
3. Scroll down to the “Get notifications from these senders” section and find “Get tips, tricks, and suggestions as you use Windows.” Toggle the switch to the off position to disable Windows tips.
4. Additionally, you can also disable specific tips by scrolling further down to the “Tips” section and toggling off any tips you don’t want to see.
5. Once you have turned off Windows tips, you should notice an improvement in your PC’s performance as it will no longer spend resources on displaying these tips.
Remember, if you ever want to re-enable Windows tips in the future, simply follow the same steps and toggle the switches back on.
By turning off Windows tips, you can optimize your Windows 10 PC’s performance and eliminate any potential distractions or interruptions caused by these tips.
Control OneDrive Syncing
1. Open the OneDrive settings: Right-click on the OneDrive icon in the notification area of the taskbar and select “Settings”.
2. Choose which folders to sync: In the “Account” tab, click on “Choose folders” and uncheck any folders that you don’t need to sync to your PC. This will reduce the amount of data being synced and free up system resources.
3. Pause syncing: In the “Settings” tab, click on “Pause syncing” to temporarily stop OneDrive from syncing files. This can be useful when you need your PC’s resources for other tasks.
4. Adjust backup settings: In the “Backup” tab, you can choose whether to back up your important folders like Desktop, Documents, and Pictures to OneDrive. Consider disabling backup for large folders that are not essential to your workflow.
5. Optimize OneDrive performance: In the “Settings” tab, click on “Optimize” and select “Files on-demand”. This feature allows you to access your OneDrive files without actually downloading them to your PC, saving storage space and reducing the impact on performance.
Remember to periodically check your OneDrive settings and adjust them based on your needs. By controlling OneDrive syncing, you can optimize your PC’s performance and reduce the strain on system resources.
Additionally, consider implementing these general tips to further improve your Windows 10 PC performance:
– Defragment your hard drive: Use the built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter to optimize the placement of files on your hard drive, improving read and write speeds.
– Keep Windows up to date: Regularly install Windows updates as they often include performance improvements and bug fixes.
– Manage startup programs: Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc and go to the “Startup” tab. Disable any unnecessary programs from starting up with your PC to reduce boot time.
– Remove unnecessary software: Uninstall any unused or unnecessary applications from your PC to free up storage space and improve performance.
– Clean up your Windows Registry: Use a trusted registry cleaner tool to remove invalid entries and optimize your system’s performance.
– Consider upgrading your hardware: If your PC’s performance is consistently slow, it may be time to upgrade your hardware components like RAM, hard drive, or processor.
Enable OneDrive Files On-Demand
1. Open the OneDrive settings by right-clicking on the OneDrive icon in the system tray and selecting “Settings”.
2. In the Settings tab, check the box next to “Save space and download files as you use them” under the Files On-Demand section.
3. Click “OK” to save the changes.
Enabling OneDrive Files On-Demand allows you to access your files in the cloud without having to download them to your computer. This can help improve the performance of your Windows 10 PC by reducing the amount of storage space used and speeding up file access.
By using Files On-Demand, you can see all your files in File Explorer, even if they are not stored locally on your PC. When you open a file that is not currently downloaded, it will be downloaded on-demand and available for use. This means you can access all your files without taking up unnecessary space on your hard drive.
Files On-Demand is especially useful if you have limited storage on your PC or if you work with large files that you don’t need to have constantly available. It allows you to free up space on your computer while still having easy access to all your files through the OneDrive app.
In addition to enabling Files On-Demand, there are other steps you can take to improve the performance of your Windows 10 PC. Regularly defragmenting your hard drive, keeping Windows and your applications up to date with the latest updates, and optimizing your startup programs can all help improve overall performance.
If you’re experiencing slow PC performance, it’s also worth checking for any malware or viruses that could be affecting your system. Running a full scan with your antivirus software can help identify and remove any potential threats.
Taking these steps and enabling OneDrive Files On-Demand can help optimize your Windows 10 PC and improve its overall performance. By managing your files efficiently and keeping your system updated, you can ensure a smoother and faster computing experience.
Disable Search Indexing
1. Open the Control Panel by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Control Panel” from the menu.
2. In the Control Panel, click on “Indexing Options.”
3. In the Indexing Options window, click on the “Modify” button.
4. Uncheck the box next to the drive or folder that you want to disable indexing for. You can also click on “Show all locations” to see a list of all indexed locations on your PC.
5. Click on “OK” to save your changes.
6. If prompted, select “Apply changes to drive X:\, subfolders and files” (where X is the drive you disabled indexing for) and click on “OK.”
7. Repeat steps 4-6 for any other drives or folders that you want to disable indexing for.
By disabling search indexing, you are preventing Windows from constantly scanning and indexing files on your PC, which can help improve its overall performance. However, keep in mind that search functionality within Windows and certain applications may be affected.
If you ever need to re-enable search indexing, simply follow the same steps and check the box next to the drive or folder you want to enable indexing for.
Remember that there are also other factors that can contribute to a slow PC performance, such as outdated software, unnecessary startup programs, or a fragmented hard drive. It’s a good idea to regularly update your Windows operating system and applications, run disk defragmentation, and consider removing any unnecessary programs or files.
If you’re using a laptop, optimizing your power settings can also help improve performance. Adjusting your power plan to “High performance” or customizing it to balance performance and battery life can make a noticeable difference.
Clean Hard Disk Space
One common cause of slow PC performance in Windows 10 is a cluttered hard disk. Over time, your hard disk can become filled with unnecessary files and data, which can impact the overall speed and responsiveness of your computer.
To clean up your hard disk space and improve your Windows 10 PC’s performance, follow these steps:
1. Open the Windows Disk Cleanup tool. You can do this by typing “Disk Cleanup” into the search bar on your taskbar and selecting the Disk Cleanup app from the search results.
2. Select the drive you want to clean. The Disk Cleanup tool will scan the selected drive for unnecessary files that can be safely deleted.
3. Review the list of file types. The Disk Cleanup tool will present you with a list of file types that can be deleted. You can select the file types you want to remove, or you can choose “Clean up system files” to include additional files such as Windows Update files and system error memory dump files.
4. Click “OK” to start the cleanup process. The Disk Cleanup tool will begin deleting the selected files from your hard disk.
5. Remove unnecessary applications. In addition to cleaning up files, it’s also a good idea to remove any unnecessary applications or programs from your PC. To do this, open the Control Panel and select “Uninstall a program” under the “Programs” section. From there, you can select the applications you want to remove and click “Uninstall” to free up space on your hard disk.
6. Clear your browser cache. Web browsers store temporary files, cookies, and other data as you browse the internet. Over time, this cache can become bloated and slow down your browsing experience. To clear your browser cache, open your web browser’s settings, locate the option to clear browsing data, and select the appropriate checkboxes to remove cache files.
By following these steps, you can clean up your hard disk space and help improve the performance of your Windows 10 PC. Regularly performing these maintenance tasks can help keep your PC running smoothly and efficiently.
Registry Cleanup
1. Open the Registry Editor by pressing the Windows key + R, typing “regedit” in the Run dialog box, and hitting Enter.
2. Before making any changes, it’s crucial to back up your registry. Go to File > Export, choose a location to save the backup file, and give it a descriptive name.
3. Once you have a backup, navigate to the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run.
4. Here, you’ll find a list of programs that start automatically when your PC boots up. Carefully review the list and delete any entries that belong to programs you no longer use or recognize. Right-click on the entry and select Delete.
5. Repeat step 4 for the following keys:
– HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
– HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
6. Next, clean up invalid file associations. In the Registry Editor, go to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT and look for file extensions that are no longer associated with any program. Right-click on the extension and select Delete.
7. Remove unnecessary startup services by going to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services. Again, carefully review the list and delete any services that are no longer needed. Right-click on the service and select Delete.
8. Finally, clean up orphaned registry keys. These are keys that are left behind by uninstalled programs. In the Registry Editor, go to Edit > Find and type in the name of the program you’ve uninstalled. Delete any registry keys associated with it.
Remember to proceed with caution when editing the registry. Making incorrect changes can cause serious issues with your system. If you’re not confident in your abilities, it’s best to seek professional help or use a trusted registry cleaning tool.
In addition to cleaning the registry, it’s also important to regularly update your Windows operating system. Windows updates often include performance improvements and bug fixes that can help speed up your PC. To check for updates, go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and click on “Check for updates”.
By performing regular registry cleanups and keeping your Windows 10 up to date, you can optimize your PC’s performance and enjoy a faster and smoother computing experience.
Simplify Visual Effects
- Disable unnecessary visual effects: Adjust the visual settings of Windows 10 to improve performance.
- Turn off transparency effects.
- Reduce or disable animations.
- Disable live tiles.
- Optimize the Start menu.
- Minimize the number of open windows and running applications.
- Remove unnecessary desktop icons.
- Use a basic or solid color desktop background.

- Disable unnecessary startup programs.
- Regularly clean up temporary files and unnecessary system files.
Turn Off Transparency

1. Open the Settings menu by clicking on the Windows Start button and selecting “Settings.”
2. In the Settings menu, click on “Personalization.”
3. From the left-hand menu, select “Colors.”
4. Scroll down until you see the “Transparency effects” option. Toggle the switch to turn it off.
5. After turning off transparency, you should notice a difference in the responsiveness and speed of your PC.
Disabling transparency can alleviate the strain on your system resources, allowing your computer to run more smoothly. This is especially beneficial for older laptops or computers with limited hardware capabilities.
In addition to turning off transparency, there are other steps you can take to optimize your Windows 10 PC’s performance. These include disabling unnecessary startup programs, cleaning up your hard drive, and updating your device drivers. By regularly maintaining your PC and optimizing its settings, you can ensure that it runs efficiently.
If you’re experiencing persistent issues with slow performance, it may be worth considering upgrading to Windows 11 or consulting with a professional for further assistance. However, for many users, disabling transparency can provide a noticeable improvement without the need for more drastic measures.
Remember, these steps are specific to Windows 10. If you’re using a different operating system, the process may vary. Always refer to the appropriate documentation or seek professional advice to ensure you’re making the right changes for your specific system.
Update Device Drivers
One common cause of slow PC performance in Windows 10 is outdated or faulty device drivers. Device drivers are software programs that allow your computer’s operating system to communicate with and control the hardware devices attached to your system. When these drivers are outdated or not working properly, it can lead to sluggish performance and other issues.
To update your device drivers and improve your Windows 10 PC’s performance, follow these steps:
1. Identify the outdated drivers: Open the Device Manager by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting “Device Manager.” Look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark or a red X next to them. These symbols indicate that the device drivers are outdated or not working correctly.
2. Download the latest drivers: Visit the manufacturer’s website for each device with outdated drivers and locate the drivers section. Look for the latest driver version compatible with your Windows 10 operating system. Download the drivers onto your computer.
3. Install the new drivers: Once the drivers are downloaded, double-click on the driver file and follow the on-screen instructions to install them. If prompted, restart your computer to complete the installation.
4. Use third-party driver update software: If manually updating drivers seems overwhelming, you can use third-party driver update software to automate the process. These programs scan your system, identify outdated drivers, and download and install the latest versions for you. Be sure to select a reputable software from a trusted source.
5. Windows Update: Windows 10 also provides automatic driver updates through Windows Update. To access this feature, go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Click on “Check for updates” and let Windows search for the latest drivers available for your system. If any updates are found, follow the prompts to install them.
Updating your device drivers can significantly improve your Windows 10 PC’s performance. By ensuring that your hardware devices are running on the latest software, you can enhance their compatibility with the operating system and optimize their performance.
Remember to regularly check for driver updates and keep your PC’s drivers up to date. This will help prevent future performance issues and ensure that your system is running smoothly.
Schedule Automatic Maintenance
1. Open the Control Panel by pressing the Windows key + X on your keyboard and selecting “Control Panel” from the menu.
2. In the Control Panel, click on “System and Security” and then select “Security and Maintenance.”
3. Under the “Maintenance” section, click on “Change maintenance settings.”
4. In the maintenance settings window, you can choose the time and frequency for automatic maintenance to run. Check the box next to “Automatic maintenance” if it’s not already selected.
5. You can also choose to allow maintenance to wake up your PC from sleep mode to perform the tasks. Check the box next to “Allow scheduled maintenance to wake up my computer at the scheduled time” if desired.
6. Click on the “OK” button to save your changes and close the window.
By scheduling automatic maintenance, Windows 10 will perform several tasks in the background to keep your PC running smoothly. These tasks include software updates, system diagnostics, disk cleanup, and disk defragmentation. It’s important to note that automatic maintenance requires your PC to be turned on and connected to a power source during the scheduled time.
Regularly scheduling automatic maintenance can help prevent software bloat, clear temporary files, and optimize the performance of your PC. It is especially useful for laptops and desktop computers that are frequently used and may accumulate unnecessary files over time.
If you have any specific questions or issues related to scheduling automatic maintenance on Windows 10, you can refer to the FAQ section on the Microsoft Windows website or seek help from online forums and communities.
Remove Unnecessary Software
- Uninstall unnecessary programs: Remove any software or applications that you no longer use or need.
- Disable startup programs: Prevent unnecessary programs from launching at startup, slowing down your PC.
- Clear out temporary files: Delete temporary files and folders that take up valuable disk space and contribute to slower performance.
- Remove bloatware: Get rid of pre-installed software that came with your PC and is often unnecessary or resource-heavy.
- Disable visual effects: Turn off unnecessary visual effects that can consume system resources and impact performance.
- Update or remove outdated drivers: Ensure that all your hardware drivers are up to date, improving compatibility and performance.
- Remove browser extensions: Disable or uninstall unnecessary browser extensions that can slow down your web browsing experience.
- Disable unnecessary services: Stop unnecessary background services that run automatically and consume system resources.
- Clean up your desktop: Remove icons and files from your desktop that can slow down your PC’s performance.
- Perform a malware scan: Use reliable antivirus software to scan and remove any malware or viruses that may be slowing down your PC.
F.A.Qs
How do I clean up my computer to make it run faster?
To make your computer run faster, you can prevent programs from automatically running at startup, uninstall unnecessary programs, clean up hard disk space by deleting unnecessary files, save old pictures or videos to the cloud or an external drive, and run a disk cleanup or repair.
Why is my PC so slow all of a sudden Windows 10?
Your PC may be slow all of a sudden on Windows 10 due to various reasons such as multiple programs running simultaneously, virus infection, malware, hardware issues, or high memory usage.
How do I fix slowness on Windows 10?
To fix slowness on Windows 10, ensure you have the latest updates for Windows and device drivers, restart your PC and only open necessary apps, utilize ReadyBoost for performance improvement, manage the page file size, and check for low disk space and free up space.